Ultraviolet light (UV) is a type of radiant energy that appears on the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum between visible light and x-rays. It has a shorter wavelength than visible light but higher energy (or frequency).
- Wavelength = distance between 2 peaks measured in nanometers.
- Frequency = number of waves over time, measured per second or Hz.
- Short wavelength = high-frequency wavelengths pass in shorter time
- Long Wavelength = lower frequency wavelengths take longer to complete
The EM spectrum has seven regions based on wavelength and frequency/energy.
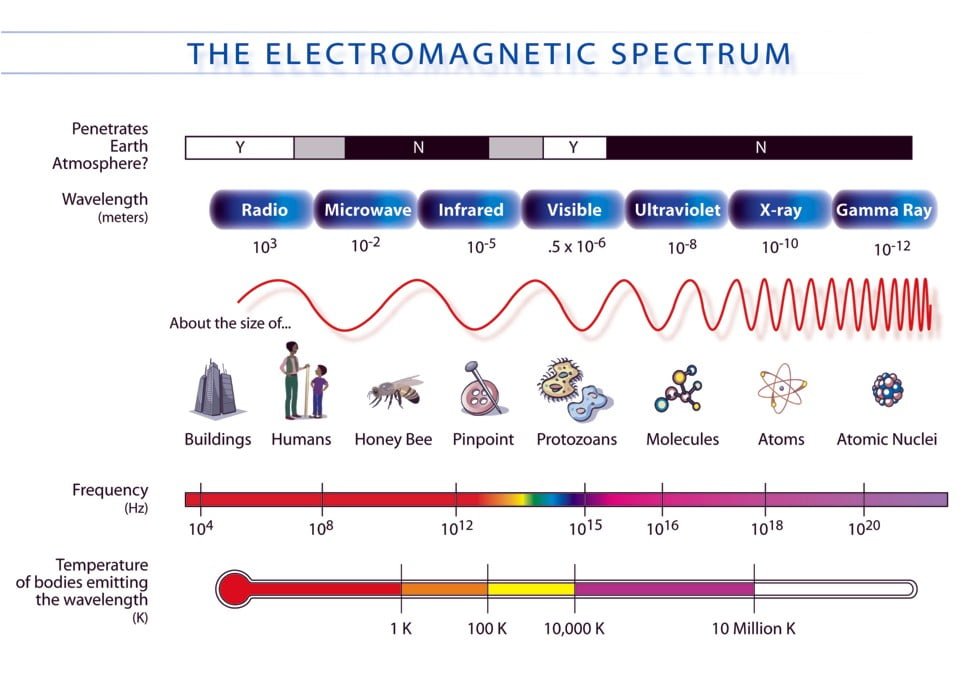
- Radio Waves –Long waves used in communications such as radio, voice, data and other media.
- Microwaves – Heat source for Microwave ovens, radar and high bandwidth communication.
- Infrared –Invisible to the human eye but is felt as heat. Think of a toaster.
- Visible Light –Can be seen by the human eye.
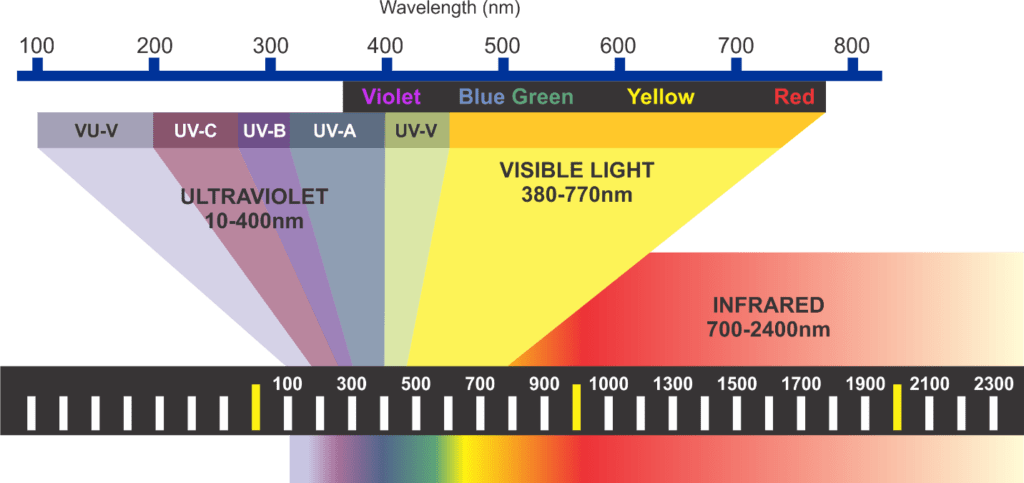
- Ultraviolet (UV) –Cannot be seen by the human eye and can be broken down further into A, B, C & V
- X-Rays –Soft x-rays are produced by accelerating electrons. Dangerous.
- Gamma Rays – Hard x-rays produced by atomic nuclei and can kill cancer cells. Very dangerous.
UV Light from the Sun vs Man-made
Sunlight contains only about 10% UV and only one-third of that UV penetrates the earth’s atmosphere. Of that one-third, 95% is UVA which has the least energy and is always present around us. It will tan your skin, causes skin cells to age, and damages DNA.
UVB accounts for the remaining 5% and is the UV that damages the DNA directly in skin cells and is responsible for causing sunburn, cataracts, and most skin cancers.
UVC has the most energy but UVC from the sun does not reach the earth’s surface because it is blocked by the ozone. UVC damages and destroys genetic material. UVC is used to purify air and water and to disinfect and sterilize. UVC can be generated or produced by passing an electric current through vaporized mercury. Artificial (man-made) UV light sources include tanning lamps, uv curing lamps, mercury vapor lamps, and germicidal lamps.
Health Benefits of UV
The warmth of the sun brings out the best in most of us. It energizes us and improves our mood. Exposure to UVB from the sun promotes vitamin D production, which has multiple health benefits, including the production of serotonin. Vitamin D promotes better sleep, stronger bones, a healthier immune system, and can lower blood pressure. Another advantage of UV is in the treatment of certain skin conditions. PUVA is a light procedure that uses UVA light exposure in combination with a drug or cream and is said to help treat vitiligo, eczema, psoriasis, and lymphoma.
Common Everyday Uses of UV Light
UV is used to dry and disinfect many products you are probably familiar with and purchase. Dentists regularly use UV to cure resins or whiten teeth and nail salons use small UV heaters to quickly dry nail polish. UV and 3D printers are used to instantly dry ink on paper or models.
While these are common uses, did you know that UV is also used to pasteurize juice and remove microorganisms in food? Apple cider and other juices are often treated with UV light to reduce microbial pathogens. UV-C is used in greenhouse irrigation to purify contaminated water to clean lettuce, vegetables, and fruit. Contaminated water can cause outbreaks of E. coli which result in widespread illness.
Germicidal Lamps
The COVID-19 pandemic saw many individuals and companies purchasing germicidal lamps to disinfect their homes and offices. When there was a shortage of N95 respirators, UV was offered as a solution to sanitize respiratory masks in hospitals. The NIH even published a study stating that N95 respiratory masks decontaminated with UV and VHP (vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide) could be reused up to three times as long as the wearer verified that the mask fits properly.
UV Curing
UV curing is a process in which high-intensity ultraviolet light is used to quickly harden inks, coatings and adhesives onto metals, wood and other surfaces. Learn more about UV curing.
UV Curing Lamps for Manufacturing
Many manufacturing industries utilize UV for the items you encounter daily. UV’s fast-drying, energy-efficient, and green technology emits no Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) and is used in the production of many products, including:
- Soda and food cans
- aerosol hairspray
- bottle caps and jar lids
- toothpaste tubes
- plastic & styrofoam cups
- pet food and garden supply bags
- hardwood and luxury vinyl tile (LVT) flooring
- packaging of all types
- automotive parts, including car windshields and headlights
- cell phone components
Space always comes at a premium in a manufacturing facility and depending on the application, adding UV curing lamps to a production line can save a company considerable space. Typical conventional thermal drying ovens for high-volume production lines can be 50 to 200 feet long, depending on the application and process speed. In contrast, a UV curing chamber for the same types of applications will only consume about 3 to 10 feet. Implementing UV curing into a production line will result in faster production speeds, shorter cycle times, and significant production and cost savings.





 简体中文
简体中文 Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español ไทย
ไทย