
What is an ARC UV System? An arc UV system comprises electrodes at each end of a tubular-shaped quartz lamp, commonly filled with a blend of mercury and noble gas. By applying electrical discharge from these electrodes within the tubular lamp, the mercury is stimulated into a plasma state, emitting light across the entire UV spectral range (approximately 200 nm to 450 nm). Its primary peaks are observed at wavelengths of 240-270 nm and 350-380 nm.
What is UV Curing?
UV curing is the process by which UV light initiates a photochemical reaction of a UV-curable solution (such as inks, coatings, or adhesives) that causes the solution to polymerize.
Benefits of Arc UV Lamp Curing
Arc UV systems hold a distinct advantage over electrodeless UV lamp systems in their versatility regarding lamp length. While electrodeless lamps are commonly available in fixed lengths of either 6 inches or 10 inches, arc lamps offer the flexibility to be tailored precisely to the width requirement of the curing process. This flexibility becomes crucial when dealing with substrates wider than 10 inches. Instead of positioning electrodeless lamps end-to-end to cover the entire width, a single arc lamp can be made to the required length to expose the entire substrate width. For instance, a substrate measuring 50 inches wide can be efficiently cured with a single 55-inch arc lamp UV bulb, whereas, if using electrodeless UV lamps, five 10 inch electrodeless lamps would be positioned end-to-end in a row to expose the 50 inch wide substrate. UV lamp maintenance is much easier and less costly for a single arc lamp vs. 5 electrodeless lamps.
Arc lamp systems will have fewer consumable parts than microwave-powered electrodeless lamp systems. Consequently, with fewer lamps in a typical UV system and fewer consumable parts per lamp, the arc lamp system will be much less costly to maintain.
Since both UV lamp technologies have advantages, the user must consider and weigh the advantages of each technology for the specific application and production process to determine the best choice.
Components of an ARC UV System
The essential components of an arc UV system include:
UV Lamp Housing Assembly
This houses the UV lamp and includes components such as a reflector and cooling system.
Reflector
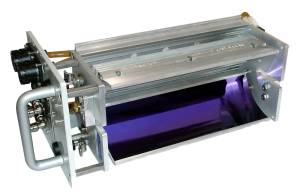
The curved reflector within the lamp housing assembly directs UV light towards the substrate, enhancing exposure intensity.
Arc UV Bulb

An arc UV lamp produces light through an electrical arc between two electrodes. The gas between the electrodes is initialized by a high-voltage current, which ionizes the gas or vapor, creating a conductive plasma.
Power Supply

Also known as a ballast for arc lamps, it provides power to the UV lamp.
Cooling System
UV lamps operate at high temperatures, and a cooling the UV lamp properly is essential to ensure long lasting UV bulbs. Arc lamp systems are commonly cooled with air. However, some arc lamps have a combination of air and water cooling. If the UV lamp is not cooled sufficiently, the result is the UV bulb itself will reach or exceed the quartz softening temperature and cause the lamp to distort in shape, and commonly turn into a banana shape. Lamps that operate at excessively high temperatures will result in shortened lamp life and UV output reduction. On the contrary, too much air cooling of the UV lamp can cause the UV lamp to become unstable and extinguish.





 简体中文
简体中文 Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español ไทย
ไทย